May
25
[原]解决启动时提示Entering runlevel 及大量avc提示的问题 

一台装有红旗安全操作系统 4.0(RedFlag Security OS 4.0)的机器,在启动时提示:
输入3后无法进入系统。按照《红旗安全操作系统4.0 安装分发手册》65页的“系统启动时出现大量avc提示后无法引导”一节的步骤操作,问题依旧。经分析,原来是/etc/inittab文件的安全标记与系统安全标记库不一致所造成的。
一、问题现象
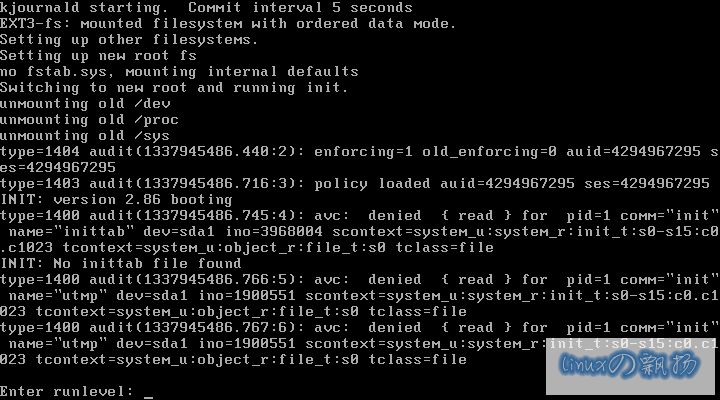
系统启动时,出现大量avc错误,并提示Entering runlevel 的界面:
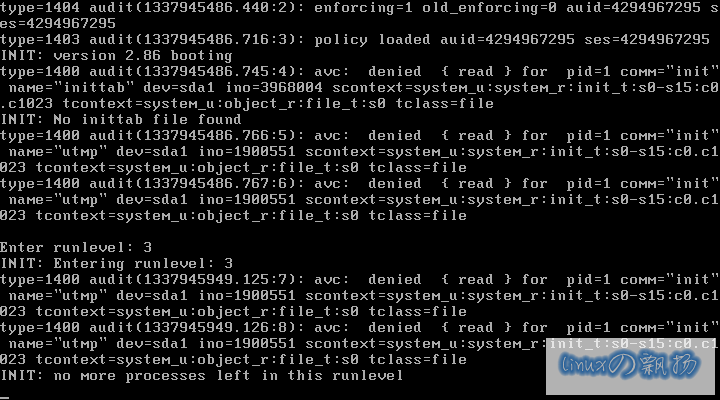
输入“3”后,仍无法引导:
二、故障分析
1.原因
按照《红旗安全操作系统4.0 安装分发手册》65页的“系统启动时出现大量avc提示后无法引导”一节的描述,该问题出现的可能,是因为当前文件系统安全标记与系统安全标记库出现不一致,需要对整个文件系统进行重新安全标记。而这个步骤,本来在系统首次安装完毕后会自动进行。
但若在后期实施部署时,在SELinux模式被禁用的情况下,对系统文件进行修改,当重新打开SELinux模式后,即可能出现类似的问题。
2.尝试
既然如此,尝试按手册中描述的重新标记步骤进行:
结果问题依旧。
3.思考
从系统提示的信息来看,原因正是上面所描述的。但重新打标记的操作不成功,可能是因为某些程序判断的问题。
查看/etc/rc.sysinit 文件,可找到:
这里的relabel_selinux 正是重打标记的操作函数。但rc.sysinit 是在inittab之后执行的,而现象中所提示的是“需输入运行级别runlevel”,由此判断,可能是inittab文件曾被修改,其安全标记已不同。换句话说,还没到执行rc.sysinit 时,已出现问题。
在从上面的代码可看到,$SELINUX_STATE 变量的状态也对重打标记有影响,在rc.sysinit 中还有:
为此,如果把enforce设为0,应可自动重打标记。
(必须已完成第一步的touch /.autorelabel 操作,否则判断不会生效的。)
三、故障解决
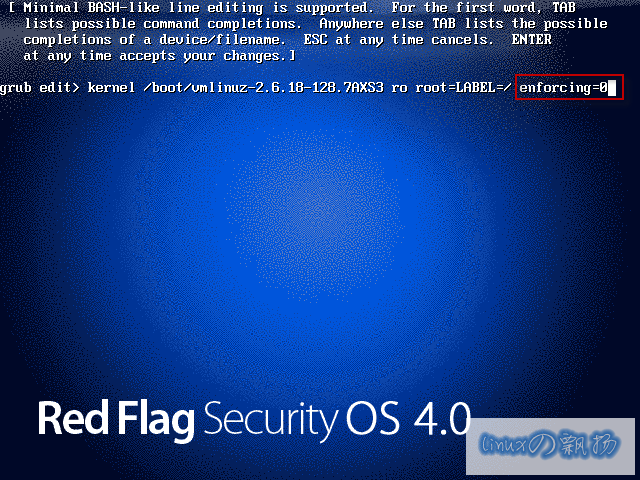
考虑上面的步骤,但在重启时,grub后面加入:
如图:
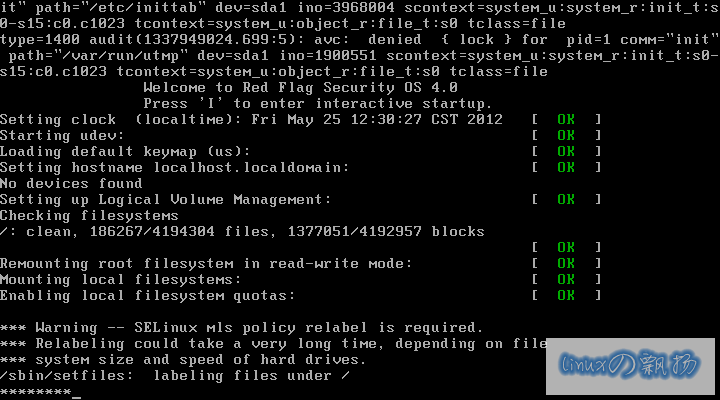
随后,系统引导时,会自动进行重新打标记的工作:
完成后,正常进入系统,重启,恢复正常。
四、参考资料
How to Disable SELinux
grub中加入的enforcing=0,使得SElinux 进入Permissive 模式,而selinux=0,是直接Disabled。两者是不相同的。系统命令setenforce的作用是类似的(/selinux/enforce),除非把SELinux修改为Disable,重启系统,否则,只是进入警告模式。
引用
Entering runlevel
输入3后无法进入系统。按照《红旗安全操作系统4.0 安装分发手册》65页的“系统启动时出现大量avc提示后无法引导”一节的步骤操作,问题依旧。经分析,原来是/etc/inittab文件的安全标记与系统安全标记库不一致所造成的。
一、问题现象
系统启动时,出现大量avc错误,并提示Entering runlevel 的界面:
输入“3”后,仍无法引导:
二、故障分析
1.原因
按照《红旗安全操作系统4.0 安装分发手册》65页的“系统启动时出现大量avc提示后无法引导”一节的描述,该问题出现的可能,是因为当前文件系统安全标记与系统安全标记库出现不一致,需要对整个文件系统进行重新安全标记。而这个步骤,本来在系统首次安装完毕后会自动进行。
但若在后期实施部署时,在SELinux模式被禁用的情况下,对系统文件进行修改,当重新打开SELinux模式后,即可能出现类似的问题。
2.尝试
既然如此,尝试按手册中描述的重新标记步骤进行:
引用
1)在grub引导项上按e键移动方向键至kernel行后再按e键,在行尾追加核心参数selinux=0后回后按b键正常引导。
2)登录后切换到root环境并执行touch /.autorelabel 命令。
3)执行reboot命令重启主机,系统会提示进行文件系统重新标记,标记完毕会成功引导。
2)登录后切换到root环境并执行touch /.autorelabel 命令。
3)执行reboot命令重启主机,系统会提示进行文件系统重新标记,标记完毕会成功引导。
结果问题依旧。
3.思考
从系统提示的信息来看,原因正是上面所描述的。但重新打标记的操作不成功,可能是因为某些程序判断的问题。
查看/etc/rc.sysinit 文件,可找到:
这里的relabel_selinux 正是重打标记的操作函数。但rc.sysinit 是在inittab之后执行的,而现象中所提示的是“需输入运行级别runlevel”,由此判断,可能是inittab文件曾被修改,其安全标记已不同。换句话说,还没到执行rc.sysinit 时,已出现问题。
在从上面的代码可看到,$SELINUX_STATE 变量的状态也对重打标记有影响,在rc.sysinit 中还有:
为此,如果把enforce设为0,应可自动重打标记。
(必须已完成第一步的touch /.autorelabel 操作,否则判断不会生效的。)
三、故障解决
考虑上面的步骤,但在重启时,grub后面加入:
引用
enforcing=0
如图:
随后,系统引导时,会自动进行重新打标记的工作:
完成后,正常进入系统,重启,恢复正常。
四、参考资料
How to Disable SELinux
引用
You need to decide if you want to disable SELinux temporarily to test the problem, or permanently switch it off. It may also be a better option to make changes to the policy to permit the operations that are being blocked - but this requires knowledge of writing policies and may be a steep learning curve for some people. For the operating system as a whole, there is two kinds of disabling:
Permissive - switch the SELinux kernel into a mode where every operation is allowed. Operations that would be denied are allowed and a message is logged identifying that it would be denied. The mechanism that defines labels for files which are being created/changed is still active.
Disabled - SELinux is completely switched off in the kernel. This allows all operations to be permitted, and also disables the process which decides what to label files & processes with.
Disabling SELinux could lead to problems if you want to re-enable it again later. When the system runs with file labelling disable it will create files with no label - which could cause problems if the system is booted into Enforcement mode. A full re-labelling of the file system will be necessary.
Permissive - switch the SELinux kernel into a mode where every operation is allowed. Operations that would be denied are allowed and a message is logged identifying that it would be denied. The mechanism that defines labels for files which are being created/changed is still active.
Disabled - SELinux is completely switched off in the kernel. This allows all operations to be permitted, and also disables the process which decides what to label files & processes with.
Disabling SELinux could lead to problems if you want to re-enable it again later. When the system runs with file labelling disable it will create files with no label - which could cause problems if the system is booted into Enforcement mode. A full re-labelling of the file system will be necessary.
grub中加入的enforcing=0,使得SElinux 进入Permissive 模式,而selinux=0,是直接Disabled。两者是不相同的。系统命令setenforce的作用是类似的(/selinux/enforce),除非把SELinux修改为Disable,重启系统,否则,只是进入警告模式。
博爱老头 



2012/06/07 22:04
SELINUX这东西很多人狠,也很多人爱,用好了会觉得很省心,用不好就会觉得他垃圾,深入研究,才发现他是多么需要的一套安全屏障。
linuxing 回复于 2012/06/11 15:53
是的,以前可以说是故意去忽略它,如果不是这次必须用到,估计也不会去学。但了解后,还是觉得有意义的。不过,资料也太少。
分页: 1/1  1
1 
 1
1 
 [原]VMware vSphere 中的“磁盘置备”选项
[原]VMware vSphere 中的“磁盘置备”选项 [原]Linux 下部署PPTP VPN -- 服务端
[原]Linux 下部署PPTP VPN -- 服务端


